What Fuels Human Trafficking?
In recognition of National Slavery and Human Trafficking Prevention Month, a look at the factors fueling human trafficking, both globally and locally.
At its most basic form, human trafficking is the buying and selling of people. It exists across continents and is facilitated through a variety of venues, but ultimately, human trafficking is an industry, and it profits from the exploitation of people.
Human trafficking has been likened to modern-day slavery, and in many respects, the similarities are obvious.
It's the 21st century and children, women and men are still being forced to work in inhumane conditions, for long hours, for little to no pay
Slavery of the past was an accepted economic practice, but today, human trafficking is a criminal activity. Historically, slavery systematically exploited specific groups of people. Today, anyone can be a human trafficking victim regardless of ethnicity, nationality, gender, age or economic status. Human trafficking is now facilitated online and through social media. Traffickers use love and affection as control mechanisms, and those victimized might not even self-identify as victims. Human trafficking is an incredibly complex issue based on dozens of contributing factors. To understand how trafficking exists today, what it looks like, and why it is sustained, we are going to explore three factors that give it fuel.
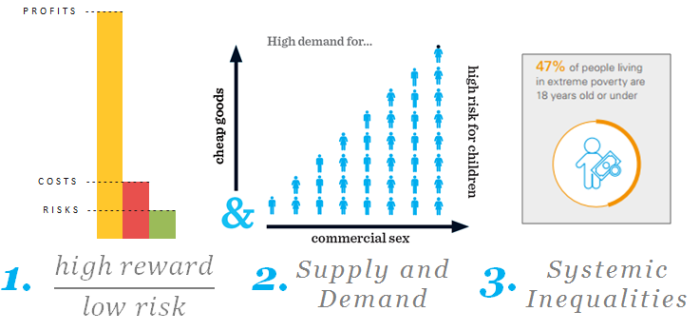
First, human trafficking is fueled by a high reward, low risk dynamic. This means that traffickers can expect to make a lot of money with minimal fear of punishment or legal consequence. It’s the second most profitable illegal industry— second only to the drug trade. And while drugs are sold in one transaction, human beings can be sold over and over again. The costs are low and the profits are extremely high. The International Labor Organization estimates that profits from human trafficking and forced labor are $150 billion annually.
But what are the risks?
The table below shows the Global Enforcement Data from the 2015 Trafficking in Persons Report. It describes the estimated amount of human trafficking prosecutions and convictions around the world each year.

The number of prosecutions is shockingly low for an industry that victimizes an estimated 21 million people around the world. Lasting legal consequences for human traffickers are still minimal and rare. Traffickers know they can sell and exploit others and little will be done to stop them.
Second, human trafficking is fueled by the economic principles of supply and demand.
Human trafficking is the only industry in which the supply and demand are the same thing: human beings. People demanding the sale of people
High demand drives the high volume of supply. Increasing demand from consumers for cheap goods incentivizes corporations to demand cheap labor, often forcing those at the bottom of the supply chain to exploit workers. Secondly, increased demand for commercial sex — especially with young girls and boys — incentivizes commercial sex venues including strip clubs, pornography and prostitution to recruit and exploit children.
Lastly, systemic inequalities and disparities make certain groups much more vulnerable to exploitation. Mass displacement, conflict, extreme poverty, lack of access to education and job opportunities, violence and harmful social norms like child marriage are all factors that push individuals into situations of trafficking. Families living in extreme poverty or families in desperate circumstances are more likely to accept risky job offers. When girls aren’t allowed to learn, parents are more likely to sell their daughters to men for marriage.
Ultimately, harmful social norms and systemic inequity fuel trafficking because traffickers target vulnerability. Traffickers look for people living in poverty, those who are desperate, those without legitimate job options, those without educational opportunities and the ones looking for a way to escape violence.
If we never address these basic human rights violations, we will never see the day when trafficking no longer exists
Want to take action? You can address the three factors that fuel trafficking by taking the following steps:
- Advocate for legislation that increases penalties for traffickers and enhances protections for victims.
- Learn how your buying habits contribute to the demand for exploitative labor by going to Slaveryfootprint.org. Then take steps to make ethical purchases by shopping for Fair Trade products. Fair Trade certification ensures that no child or slave labor contributed to the making of a product.
- Support UNICEF’s humanitarian work for vulnerable children around the world.
Learn about how UNICEF is working to ensure that every child is protected and respected. Support UNICEF. Donate today.
HOW TO HELP
There are many ways to make a difference
War, famine, poverty, natural disasters — threats to the world's children keep coming. But UNICEF won't stop working to keep children healthy and safe.
UNICEF works in over 190 countries and territories — more places than any other children's organization. UNICEF has the world's largest humanitarian warehouse and, when disaster strikes, can get supplies almost anywhere within 72 hours. Constantly innovating, always advocating for a better world for children, UNICEF works to ensure that every child can grow up healthy, educated, protected and respected.
Would you like to help give all children the opportunity to reach their full potential? There are many ways to get involved.



